In the previous article, we introduced the application of hot-melt extrusion technology in the development of amorphous solid dispersions in pharmaceutical formulation. Spray drying (SD) is another common method for preparing amorphous solid dispersions. It involves dissolving solid substances including API, polymers, and surfactants into a solvent, and then using a spray drying device to atomize the solution, allowing it to come into contact with heated gas, rapidly evaporating and drying to obtain amorphous solids. Spray drying methods have been widely used in the development of poorly soluble drug formulations due to the relatively mature process from small-scale testing to commercial production, which fully complies with the requirements of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). Table 1 lists some drugs that have been marketed using spray drying technology to prepare amorphous solid dispersions.
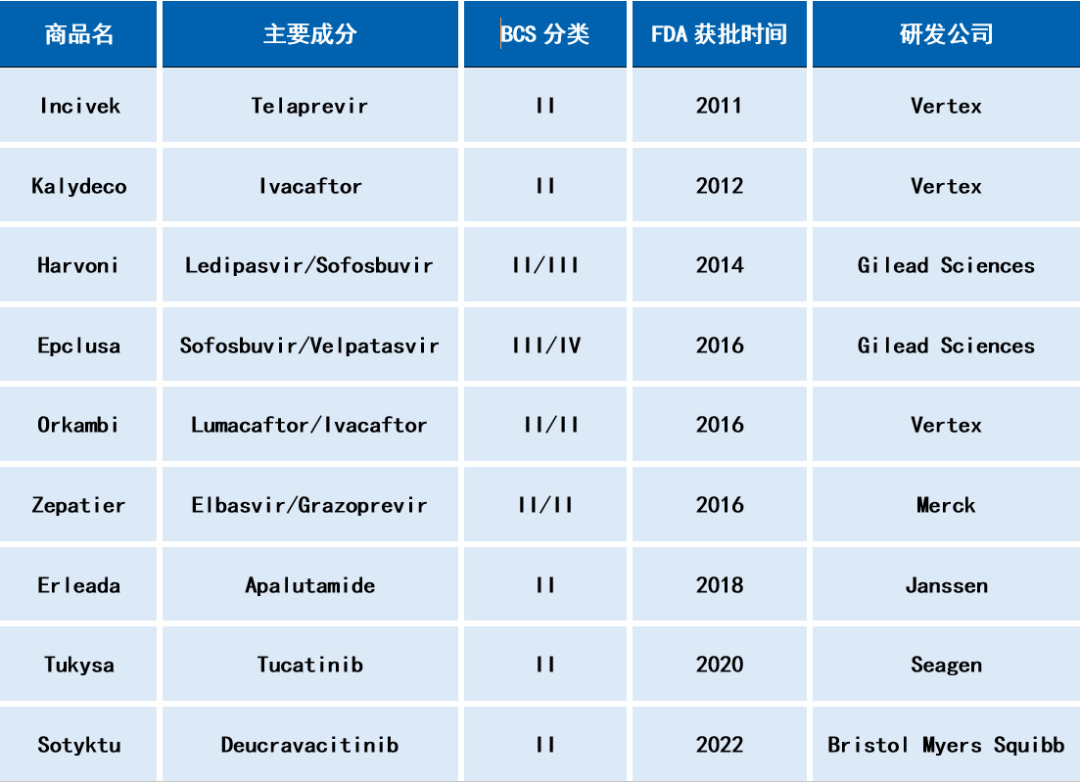 Table 1: Oral formulations on the market using spray drying technology (examples)
Table 1: Oral formulations on the market using spray drying technology (examples)
The schematic diagram of a spray drying system is shown in Figure 1. The spray drying process mainly includes:
Solution preparation: dissolving API and excipients to form a homogeneous solution;
Spray drying: atomizing the solution into fine spray using a nozzle, allowing the spray to come into contact with hot drying gas, almost instantly evaporating the liquid to form solid particles;
Cyclone separation: conveying the dried particles to a cyclone separator for separation from the gas.
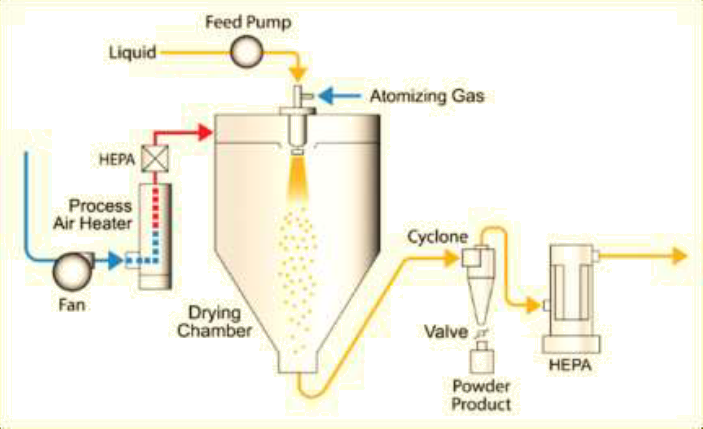
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the spray drying process
 Figure 2: Spray Dryer Used by Crystal Pharmaceuticals
Figure 2: Spray Dryer Used by Crystal Pharmaceuticals
(Buchi B-290;GEA PSD-1)
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spray Drying in Amorphous Solid Dispersion (ASD) Preparation:
Advantages:
Minimal API Quantity in Early Development: Requires a small amount of API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) in the early development stages, often in the gram-scale.
Overcoming Heat Sensitivity and High Melting Point: Effective in addressing the solubility challenges of heat-sensitive and high-melting-point APIs.
Versatility in Solvent Systems: Allows for experimentation with various solvent combinations to achieve optimal dissolution performance.
Excellent Compressibility of Intermediate: The intermediate produced by spray drying is highly compressible, facilitating downstream granulation and tablet compression processes.
Relatively Uniform Particle Size: Adjustable process parameters in spray drying can yield particles of different sizes and morphologies, providing versatility for final formulation options.
Disadvantages:
Higher Costs: The equipment for spray drying is relatively expensive, and the process consumes a significant amount of organic solvents, making it energy-intensive and costlier.
Equipment Dependency in Scale-Up: Ensuring that the spray-dried particles maintain the same characteristics (e.g., form, size, and density) as in small-scale trials can be challenging and equipment-dependent.
Lower Solvent Efficiency: Due to solubility and viscosity limitations, the solid content in the solution is typically below 10%, resulting in lower solvent utilization efficiency for spray-dried solids.
Environmental Concerns: Spray drying is less environmentally friendly compared to traditional processes that do not require organic solvents. It requires specific facility configurations and management. Even with closed-loop systems, the evaporation of a significant amount of organic solvents is challenging to recycle. Additionally, many low-boiling-point organic solvents are toxic, flammable, and require separate explosion-proof facilities.
(Note: These disadvantages are relative, and ongoing improvements in spray drying equipment and processes, along with continuous technological innovations, are better managing these challenges. Due to its applicability to a wide range of drug molecules and its inherent advantages, spray drying has become one of the most widely adopted methods for preparing amorphous solid dispersions.)
Deucravacitinib
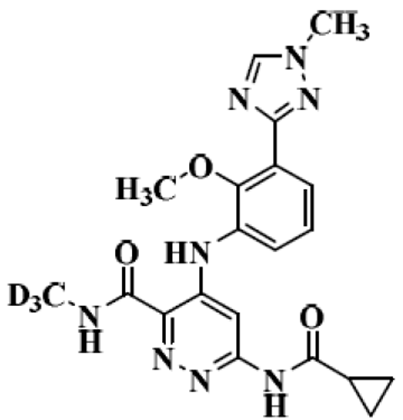
the structure of Deucravacitinib
In this case study, Deucravacitinib, which was approved in the United States in September 2022 for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adult patients suitable for systemic therapy or phototherapy, is discussed. It is the world's first approved oral selective tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) modulator, marketed under the brand name Sotyktu, available in a 6 mg oral tablet formulation. The innovator company, Bausch Health, predicts peak sales of up to $4 billion for this drug.
Deucravacitinib is classified as a BCS Class II drug, which means it has low solubility but high permeability. Its solubility is pH-dependent, with higher pH levels resulting in lower solubility. For example, at pH 1.05, the solubility of the free base crystal form is greater than 3 mg/mL, while at pH 6.5, it is only 0.009 mg/mL. To address this pH-dependent solubility and improve drug performance, the innovator company conducted research into various salt forms and crystalline polymorphs. They discovered that the hydrochloride salt form exhibited higher bioavailability and reduced pH dependence compared to the free base and other salt forms. In dogs, the hydrochloride salt form had an average bioavailability 60% higher than the free base. Consequently, the hydrochloride salt form was chosen for the early clinical trials, formulated as capsules.
However, the hydrochloride salt of Deucravacitinib was prone to racemization, which required the capsules to be stored under refrigeration for extended periods to prevent conversion to the free base during storage. This significantly increased the drug storage costs and inconvenience. To enable long-term storage at room temperature while maintaining high bioavailability and low pH dependence, a new formulation strategy was implemented during Phase III clinical trials—amorphous solid dispersion (ASD). In this method, the free base crystal form of the drug was mixed with hydroxypropyl cellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS) in a solvent mixture of acetone and water to form a solution. The solution was then spray-dried to create an ASD, which was subsequently mixed with excipients, granulated, milled, blended, and compressed into final products—film-coated immediate-release tablets. This formulation achieved an absolute bioavailability of up to 99%.
In this case, the innovator company initially selected the hydrochloride salt as the active form due to its enhanced bioavailability and reduced pH dependence. However, concerns about racemization and the need for refrigeration during storage led to further optimization of both the solid form of the drug and the formulation strategy. Ultimately, the free base crystal form was chosen as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), and an amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) was developed using spray drying to significantly improve solubility and bioavailability while addressing the pH dependence issue. This optimized formulation allowed for long-term storage at room temperature and achieved high bioavailability.
Crystal Pharmaceutical's core team possesses backgrounds in polymer materials, chemical engineering, and mechanics, guided by principles of rheology and engineering. They have extensive experience in both fundamental theory and large-scale processes, and have led formulation teams to successfully bring blockbuster SD drugs to market. Leveraging our world-class process equipment and analytical instruments for small- to large-scale processes, we have the confidence to assist global innovative pharmaceutical companies in providing high-quality drugs based on spray drying technology.