11 Apr 2025
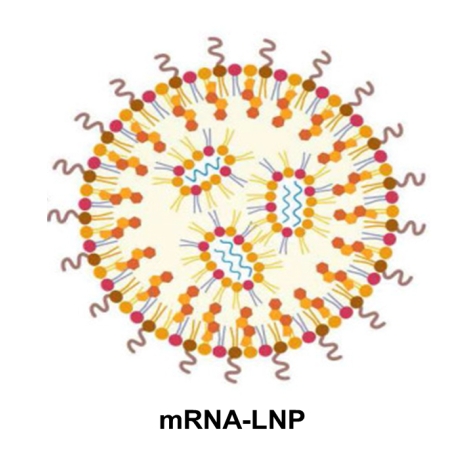
“Figure 1. mRNA encapsulated with LNP typically composed of encapture nucleic acids such as mRNA, siRNA, etc. as shown in the blue curve line by lipid nanoparticle, LNP as ionized, pegylated, phospho-lipids (dot with tails in ascending orange extent, respectively) along with cholesterol (diamond shape) (Ref: adapted from the drawing of June and Lee et al, Theranostics 2022).8
With an ever-increasing interest in designing mRNA-based vaccines, mRNA-Lipid nanoparticles (mRNA-LNP) formulation is a relatively new modality. This white paper series first discusses numerous quality attributes with influencing potency, stability, toxicity, and risk assessment relevant to mRNA-LNP modality.
There have been several good reviews to assess CQA in different modalities.1-3Critical quality attributes are measurable physical, chemical, biological, or microbiological properties within an appropriate limit, range, or distribution to ensure product quality. These attributes include identity, sterility, potency, safety, and purity, and are vital quantifiable parameters essential for maintaining the consistency and reproducibility of a drug throughout its entire life cycle.5
ICH Guidelines Q84, Q96, and Q107 provide a systematic framework for delineating critical quality attributes (CQAs), designing the product's operational range, detailing the manufacturing process, and establishing the control strategy. Due to the structural complexity of molecules and elaborate manufacturing process, it is often difficult to fully evaluate the impact of the large number of quality attributes related to safety and efficacy1. Thus, an integrated control strategy must be developed and refined over time for process characterization spanning the product's lifecycle.1
A typical mRNA molecule comprises a 5' cap and a polyadenosine (poly(A) tail at the 3' end. The 5' cap region is followed by the 5' untranslated region (5' UTR), with the 3' UTR occurring just before the poly(A) tail. These UTRs flank the coding sequence of the gene intended for expression.3

Fig: 2 Schematic diagram showing key structural features of mRNA molecule.3
The 5' cap structure facilitates mRNA binding to ribosomal initiation factors, while the 3' poly(A) tail plays a role in ribosomal machinery binding. The mRNA is typically encapsulated in delivery vehicles such as LNPs, which facilitate mRNA entering the cell cytoplasm and protect it from nuclease degradation.3
While the complete list of CQAs for mRNA-LNP is always product-specific; several common CQAs apply to all products. Five main categories of CQAs have been identified as follows: 3
(1) Purity and Product-related impurities
(2) Safety evaluation tests
(3) Strength, identity, and potency
(4) Product quality and characteristics
(5) Other obligatory CQAs
Table: 1 Category of Quality Attribute relevant to CQA unique for RNA products, precedence case in regulatory, and impact on mRNA-LNP Therapeutics.3
Category of Quality Attribute | CQA(mRNA) | Regulatory Precedence? | Impact on 3 mRNA-LNP Therapeutics |
Purity • Percentage-capped mRNA • Poly(A) tail length and distribution • RNA integrity • Percentage poly(A) mRNA | Yes Yes Yes Yes | Yes Yes Yes Yes |
The percentage of capped and polyadenylated mRNA, along with the length and distribution of the poly(A) tail, directly impact the translational efficiency
|
Process-related impurities • Residual nucleoside 5' Triphosphate (NTP) • Residual enzyme • Residual DNA template • Residual solvents • Lipid-related DP impurities • dsRNA | Yes No No No No No | Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes |
An increased level of contaminants affects the efficacy of mRNA and might trigger undesired immune reactions. |
Safety • Bioburden • Sterility • Endotoxin | No No No | Yes Yes Yes | The presence of endotoxins in pharmaceutical products could pose risks to human health upon administration.
|
Identity • Lipid ID • Sequence ID Potency • Drug Product • Drug Substance Strength • mRNA Content • RNA ratio | No No No No No No | Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes |
The accurate sequence of mRNA is crucial to produce the desired protein effectively. The lipid composition of LNP plays a crucial role in delivering mRNA into cells and impacts the product's efficacy. If more than one RNA species |
Product Quality and Characterization • Encapsulation efficiency • Surface charge • LNP Size • LNP polydispersity • Lipid content | No No No No No | Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes |
Impurities resulting from the LNP encapsulation process, lipid raw material, and lipid degradation byproducts impact the safety and efficacy of mRNA products. |
Compendial Testing (Obligatory CQAs) • Appearance • pH • Moisture content • Osmolality • Sub-visible particle • Extractable volume |
No No No No No No |
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes |
There is minimal impact of compendial testing on mRNA-LNP Therapeutics. |
As per ICH Q95 regulatory guidelines a risk assessment must be conducted for each QA for potential patient impact. The relationship between the attribute and the product’s clinical performance (PK, PD, Efficacy, and safety) should be rigorously evaluated, using prior knowledge with sound scientific judgment. Typically, this involves employing a scoring system that considers the impact and uncertainty of each attribute. The impact and uncertainty factors are scored independently against scales of up to five levels, with higher weighting assigned to the impact factor reflecting its higher importance.1 (Table 2)
Table 2. Overview of CQA Risk Ranking Methodology1 | |
Impact Assessment | Uncertainty Assessment |
Consider the known or potential effects on safety and effectiveness, including: • Safety (toxicity) • Immunogenicity • Biological Activity • PK/PD | Evaluate the significance of the following information sources: • Clinical Experience • Non-Clinical studies • Literature • Prior knowledge, platform knowledge • Invitro data |
3 - 5 levels: Scores (2 to 20) (Very high), High, moderate, low, (very low/ no effect) | 3 – 5 levels: Score (1 to 7) (Very High), high, moderate, low, (very low) |
Criticality (Risk Score) = Impact X Uncertainty1 | |
The scoring matrix combines five levels of impact with five levels of uncertainty. This yields a risk score ranging from 2 to 140. Once a cutoff score is established, attributes below the cutoff are designated as non-critical Quality Attributes (nCQA), while those above are categorized as Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs). | |
The FDA recommends a tier-based approach for assessing quality attributes, with each attribute assigned to one of three tiers based on its criticality. Criticality is determined by evaluating potential clinical impact and uncertainty. Tier 1 is reserved for attributes with the highest criticality, directly impacting the mode of action. Tier 2 is for attributes of moderate criticality. Tier 3 encompasses characteristics with the lowest criticality. Factors beyond criticality, such as analytical methodology and risk assessment, also influence the final tier assignment of each quality attribute or analytical test.
Crystal Bio is a leading Contract Research Organization (CRO) specializing in comprehensive analytical services for biotherapeutics. Our expertise covers a wide range of modalities, including mRNA-LNP Therapeutics with our strategic partner CATUG, Monoclonal Antibodies, Fusion Proteins, and Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs). With a robust analytical toolkit comprising, High-resolution LC-MS, IPRP-LC, RPLC, LC-LSD, LC-CAD, CE, cIEF, qPCR, ELISA, Endotoxin, Sterility, Bioburden, and Cell-based Bioassay, etc. Our capabilities also extend to method development and analytical characterization of biotherapeutics. This holistic approach ensures compliance with stringent regulatory requirements outlined in the CMC section, making us a valuable partner for pre-IND, Phase I, and subsequent submissions.
1. Critical Quality Attributes Assessment and Testing Strategy for Biotherapeutics Development. American Pharmaceutical Review 2019.
2. Rational selection, criticality Assessment, and tiering of Quality Attributes and test methods for analytical similarity Evaluation of Biosimilars Vandekerckhove K. et al.The AAPS Journal (2018) 20: 68
3. Defining the required critical quality attributes (CQAs) and phase requirements for mRNA/LNP product development and manufacture © BioPhorum Operations Group Ltd July 2023
4. ICH Guidelines Q8 (R2) Pharmaceutical development. 2009.
5. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/unveiling-pillars-success-setting-critical-quality-attributes/
6. ICH Guidelines Q9 Quality risk management. 2006
7. ICH Guidelines Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System. 2009
8. Lipid nanoparticles for delivery of RNA therapeutics: Current status and the role of in vivo imaging Han Na Jung, Seok-Yong Lee, Somin Lee, Hyewon Youn, Hyung-Jun Im, Theranostics 2022; 12(17): 7509-7531.


